line_profiler is a pip package that can be used to profile python code, and get a result with line-by-line execution details.
Usage:
-
Create your python file with an annotated function that you’d like to profile
import numpy as np @profile def BoxMuller(N): theta = np.random.uniform(low=0, high=2 * np.pi, size=N) E = np.random.exponential(scale=1, size=N) X = np.cos(theta) * np.sqrt(2 * E) # f(theta, E) return X if __name__ == '__main__': BoxMuller(10_000) -
Run the file with kernprof:
kernprof -l box_muller.pyThis will generate an
lproffile that can be analyzed with line_profiler: -
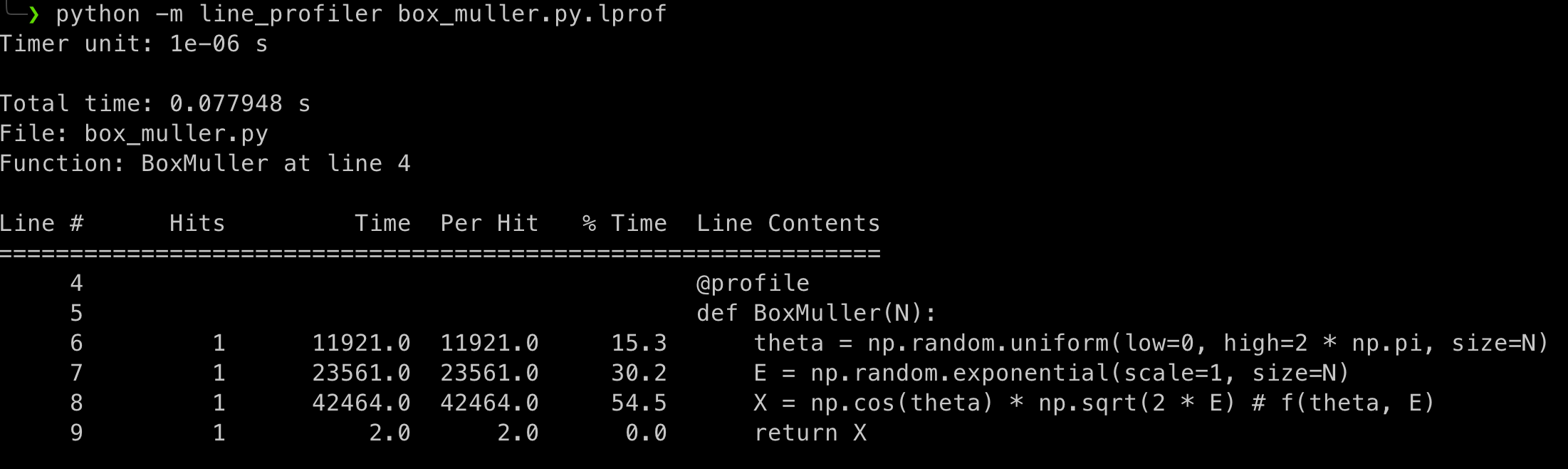
Obtain the metrics:
python -m line_profiler box_muller.py.lprof Timer unit: 1e-06 s Total time: 0.077948 s File: box_muller.py Function: BoxMuller at line 4 Line # Hits Time Per Hit % Time Line Contents ============================================================== 4 @profile 5 def BoxMuller(N): 6 1 11921.0 11921.0 15.3 theta = np.random.uniform(low=0, high=2 * np.pi, size=N) 7 1 23561.0 23561.0 30.2 E = np.random.exponential(scale=1, size=N) 8 1 42464.0 42464.0 54.5 X = np.cos(theta) * np.sqrt(2 * E) # f(theta, E) 9 1 2.0 2.0 0.0 return X
Here’s an example without wrapping:
It can even be run in Jupyter notebooks with the use of the %line_profiler extension (source):
!pip install line_profiler
%load_ext line_profiler
def test_function():
# some intense calculations
%lprun -f test_function test_function()