Given a coin, estimate the fraction of heads you would get if you flipped the coin an infinite number of times. It, of course, depends on the evidence that we see in the first flips.
The confidence in our estimate depends on two things:
- Size of the sample (100 vs 2)
- Variance of the sample (all heads vs. 52 heads)
As the variance grows, we need larger samples to have the same degree of confidence.
Error bars: graphical visualization of the variability of the data. A way to visualize uncertainty.
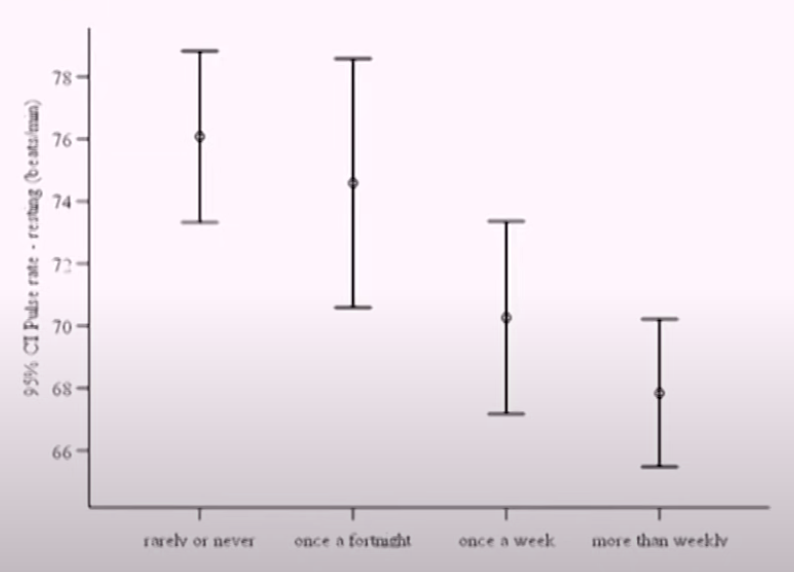
When confidence intervals (error bars) overlap, we canot say that the difference is significant. But otherwise, we can concluse that the means are statistically significantly different.